You must have heard a bank executive saying something like “Please fill the NACH form” or “Activate NACH for EMI payment”. Most people hear this word many times, but still feel confused about what NACH actually is and how it helps in daily life.
See, in today’s time, we all have monthly payments, electricity bill, water bill, mobile bill, loan EMI, insurance premium, credit card bill, subscriptions, and many more. If you try to pay everything manually, it becomes a headache. One date you forget, late fine gets added. Another time bank is closed. Sometimes you are not even in the same city.
That is where NACH comes in and simply says:
“Don’t worry. Give permission once, I’ll handle the rest every month.”
But the problem is, many people don’t properly understand NACH. Some think NACH is only for EMI. Some think it is risky for the bank account. Some students even believe that NACH can block their account. All these are misunderstandings.
In this post, we will explain everything in very simple English:
- What is the full form of NACH
- How NACH works
- Difference between NACH debit and credit
- Benefits of NACH
- Why it actually makes life easier
No technical language, no boring banking terms.
NACH Full Form: What Does It Actually Mean?
First, let’s clear the basics.
NACH = National Automated Clearing House
Now break it:
- National : Works all over India
- Automated : Runs automatically
- Clearing : Payment transfer process
- House : Centralized system
In simple words, NACH is a national system that automatically handles recurring payments. Whether it is EMI, electricity bill, insurance premium, or subscription, NACH takes care of it without manual effort.
Real-Life Example to Understand NACH
Let’s suppose you’ve taken a home loan of 30 lakh rupees. Now you have to pay an EMI of 30,000 rupees every month.
Earlier system:
- Days 5-6 of every month: You would go to the bank branch
- Stand in line for 30-45 minutes
- Fill out a form and issue a cheque
- Sometimes the payment would be late, sometimes there would be processing issues
- Your credit score would also be affected if the payment was late
But in the age of NACH:
- You fill out and submit the mandate once
- After bank verification, NACH is activated
- Now, 30,000 rupees is automatically deducted on the 5th of every month
- No tension, no lines, no forms
- Payment history is automatically updated
- Your credit score also improves because the payment is never late
That’s it! That’s the real benefit of NACH!
NACH Full Form and Meaning – Detailed Breakdown
Now, NACH is a centralized system created by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). This system automatically processes high-volume, recurring payments.
Who Is Involved in the NACH System?
| Entity | What Is the Role |
|---|---|
| NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India) | Creates and operates the NACH platform. Sets all the rules |
| Your Bank (Destination Bank) | Debits or credits your account |
| Lender / Company (User Institution) | The company you are giving the mandate to – like a bank, insurance, or utility company |
| Sponsor Bank | Processes the transaction on behalf of the lender |
| You (Customer) | Approves the mandate and authorizes the payment |
What payment options does NACH offer?
NACH is basically of two types:
1. NACH Debit (Most Common)
This happens when money is automatically deducted from your account. You have control over how much is deducted and when.
When is it used?
- 💳 Loan EMI payments (home loan, personal loan, car loan)
- 📱 Utility bills (electricity, water, phone, internet)
- 🏥 Insurance premiums (life insurance, car insurance, health insurance)
- 🎯 Subscription services (gym, OTT subscriptions)
- 💰 Credit card bills
- 📚 Education fees
- 🏠 Property tax, municipal taxes
Nach Debit Real-Life Example:
You get a phone line from Airtel for 1500 rupees per month. Previously:
- Every month you would receive a message saying, “Pay now or lose connection.”
- You would make the payment online.
- Sometimes you would forget.
- The bill would be late.
- A penalty would be applied.
Now, in the age of NACH (National Automated Clearing House):
- Fill out the NACH form with Airtel just once.
- After bank approval, 1500 rupees will be automatically deducted every month.
Bill paid! No tension, no penalties, no late charges!
2. NACH Credit (For Companies)
This happens when money is automatically credited to your account. Like salary, pension, subsidy, incentives, etc.
When is it used?
- 💼 Monthly salary payments (companies pay their employees through NACH)
- 🏛️ Government pensions (retirement pensions)
- 🚜 Subsidy distributions (agricultural subsidies, PM Kisan Yojana)
- 📈 Dividend payments (share dividends)
- 💵 Interest payments (bank interest credits)
- 🎁 Incentives and bonuses
NACH Credit Real-Life Example:
A private company has 500 employees.
Before:
- HR had to print checks every month.
- Checks had to be distributed to each employee.
- Waiting for checks to clear.
- Processing time: 2-3 days.
- Risk of check loss or bouncing.
Now with NACH Credit:
- HR sets up NACH once.
- Salaries are credited directly to everyone’s accounts on the 25th of every month.
- Instant! Zero risk, zero paperwork.
- Money goes directly into employees’ bank accounts!
Difference Between NACH Debit and NACH Credit
| Aspect | NACH Debit | NACH Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Money goes OUT from your account | Money comes IN to your account |
| Who Starts It? | Company / Lender (with your permission) | Company / Government (with your permission) |
| Example | EMI, bills, insurance premiums | Salary, pension, subsidy |
| Frequency | Fixed or variable (depends on the bill) | Usually monthly |
| Type of Transaction | Payment collection (you are paying) | Payment distribution (this is your income) |
| Typical Users | Customers / Borrowers | Employees / Pensioners |
| Real-World Scenario | You gave ICICI Bank authority to cut loan EMI through NACH | You gave your company authority to deposit salary through NACH |
How NACH Works – Step-by-Step Process
Now let’s understand how NACH actually works in the process. Let’s say you took a home loan from Bank:
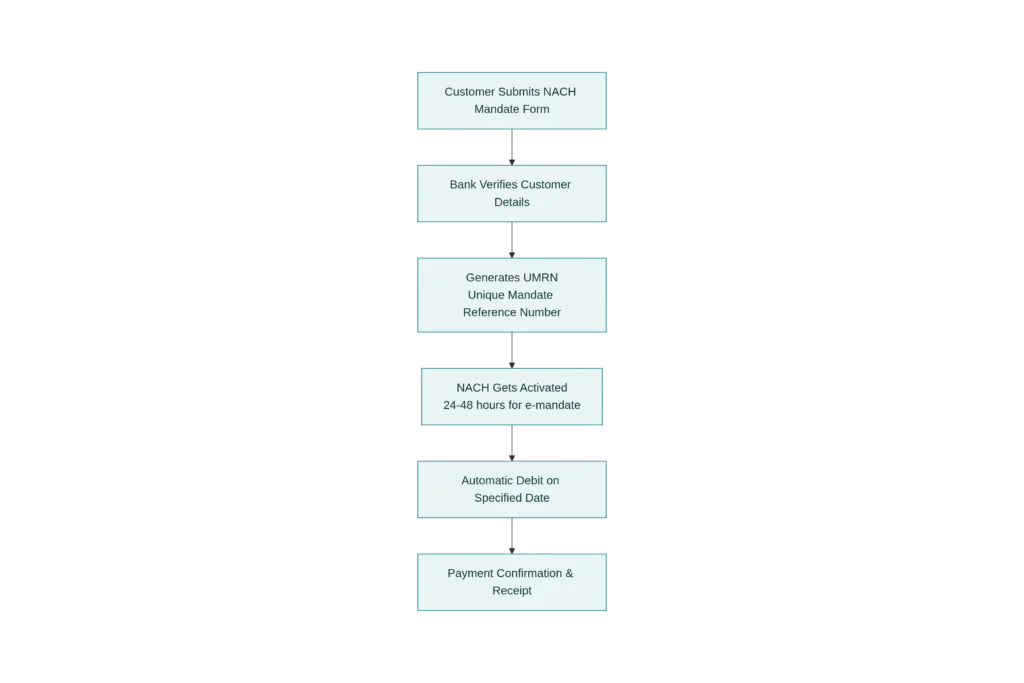
Detailed Step-By-Step Explanation:
Step 1: Fill the Mandate Form
- Fill out the NACH mandate form
- Fill your name, account number, bank details, and IFSC code
- Decide on the EMI amount and payment date
- Sign the form
Step 2: Submit to the Bank
- Submit this form to your bank branch
- Or create an online e-mandate (through net banking or the app)
Step 3: Bank Verification
- Your bank verifies your details
- It checks if there is sufficient balance in the account and if the account status is correct
- Verification is usually completed within 24-48 hours
Step 4: UMRN Number Will Be Generated
- UMRN = Unique Mandate Reference Number
- This is a unique ID for the NACH mandate
- The bank or company will send you this number via message
- This number is important for canceling or modifying the mandate in the future
Step 5: NACH Activated!
- Now your NACH mandate is active!
- Automatic debits will start from the next payment date
Step 6: Auto-Debit Every Month
- On a fixed date (like the 5th of every month)
- The exact amount (like 30,000) is automatically debited
- A confirmation message is received within 2 hours
- The amount is deducted from your account
Step 7: Payment Status Update
- The bank marks “Payment received” in its records
- The lender also receives a notification
- Your loan status is updated
Actual Real-Life Scenario: Priya’s Story
Let’s take a real-life example to understand this. There’s a girl named Priya in Delhi. She:
- Took a home loan of 1 crore rupees from HDFC Bank
- Monthly EMI: 85,000 rupees
- Payment date: 10th of every month
How Priya Set Up NACH:
| Step | What Happened | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Took form from HDFC and filled it | Name: Priya Sharma, Account No: 50123456789, EMI: 85,000, Date: 10th | 1st Jan |
| Submitted the form at HDFC branch | Cheque book and ID proof submitted along with it | 1st Jan |
| Bank verification process started | HDFC checked everything in their system | 2–3 Jan |
| UMRN number generated and message received | UMRN: MH123456789ABCD1 | 3rd Jan |
| NACH got activated | Status: Active, ready for debit | 4th Jan |
| First automatic debit | 85,000 automatically deducted | 10th Jan |
| Confirmation SMS received | “85,000 debited for EMI. Balance: 215,000” | 10th Jan (2 PM) |
| Next auto-debit | Again 85,000 deducted | 10th Feb |
| Next auto-debit | Again 85,000 deducted | 10th Mar |
| … | … | … (every month) |
When Does NACH Get Activated : E-NACH vs Physical?
| Type | Time Taken |
|---|---|
| E-NACH (Online) | 24–48 hours |
| Physical NACH | 5–10 working days |
No. NACH is not only known for EMI. It is also used for bills, subscriptions, insurance, salary, pension, and government subsidy.
Yes, NACH is completely safe. It is operated by NPCI and regulated by RBI, with proper security and verification.
No, NACH cannot block your account. It only deducts the approved amount on the selected date.
UMRN is a Unique Mandate Reference Number. It is used to track, modify, or cancel a NACH mandate.
e-NACH usually takes 24 to 48 hours, while physical form may take 5–10 working days.
